Which Of The Following Liabilities Is Created When A Company Receives Cash For Services
Current Liabilities
72 Identify and Describe Current Liabilities
To assistance in understanding electric current liabilities, assume that yous own a landscaping company that provides landscaping maintenance services to clients. As is common for landscaping companies in your area, yous require clients to pay an initial deposit of 25% for services before you begin working on their property. Asking a customer to pay for services before y'all take provided them creates a electric current liability transaction for your concern. As you've learned, liabilities require a hereafter disbursement of assets or services resulting from a prior business activeness or transaction. For companies to make more informed decisions, liabilities need to be classified into 2 specific categories: current liabilities and noncurrent (or long-term) liabilities. The differentiating factor between current and long-term is when the liability is due. The focus of this chapter is on current liabilities, while Long-Term Liabilities emphasizes long-term liabilities.
Fundamentals of Current Liabilities
A current liability is a debt or obligation due within a company'southward standard operating period, typically a twelvemonth, although at that place are exceptions that are longer or shorter than a year. A visitor's typical operating period (sometimes chosen an operating cycle) is a year, which is used to delineate current and noncurrent liabilities, and current liabilities are considered short term and are typically due inside a twelvemonth or less.
Noncurrent liabilities are long-term obligations with payment typically due in a subsequent operating menstruation. Current liabilities are reported on the classified residual sheet, listed before noncurrent liabilities. Changes in current liabilities from the commencement of an accounting period to the end are reported on the statement of cash flows as role of the cash flows from operations department. An increase in current liabilities over a menstruum increases cash flow, while a decrease in electric current liabilities decreases greenbacks menstruation.
| Current vs. Noncurrent Liabilities | |
|---|---|
| Electric current Liabilities | Noncurrent Liabilities |
| Due within i twelvemonth or less for a typical one-year operating period | Due in more than one year or longer than ane operating period |
| Short-term accounts such as:
| Long-term portion of obligations such as:
|
Examples of Electric current Liabilities
Common current liabilities include accounts payable, unearned revenues, the current portion of a note payable, and taxes payable. Each of these liabilities is current because it results from a past business action, with a disbursement or payment due within a flow of less than a yr.
Proper Current Liabilities Reporting and Calculating Burn down Rate
When using financial data prepared by accountants, decision-makers rely on ethical accounting practices. For case, investors and creditors look to the electric current liabilities to assist in computing a company'southward annual burn rate. The burn rate is the metric defining the monthly and annual cash needs of a company. It is used to assist calculate how long the company can maintain operations earlier becoming insolvent. The proper classification of liabilities as current assists decision-makers in determining the short-term and long-term greenbacks needs of a company.
Another mode to think about burn rate is as the amount of greenbacks a company uses that exceeds the corporeality of cash created past the company'due south business operations. The fire charge per unit helps indicate how apace a company is using its cash. Many kickoff-ups have a high cash burn charge per unit due to spending to first the business organization, resulting in depression cash flow. At get-go, starting time-ups typically practise not create enough greenbacks catamenia to sustain operations.
Proper reporting of current liabilities helps decision-makers empathise a company's burn charge per unit and how much cash is needed for the company to come across its brusk-term and long-term cash obligations. If misrepresented, the greenbacks needs of the company may not exist met, and the visitor can quickly exit of business. Therefore, information technology is important that the auditor appropriately report current liabilities considering a creditor, investor, or other decision-maker's understanding of a visitor's specific cash needs helps them brand skilful financial decisions.
Accounts Payable
Accounts payable accounts for fiscal obligations owed to suppliers afterward purchasing products or services on credit. This account may exist an open credit line between the supplier and the company. An open credit line is a borrowing agreement for an amount of money, supplies, or inventory. The selection to borrow from the lender can be exercised at any time within the agreed fourth dimension menstruum.
An account payable is commonly a less formal arrangement than a promissory note for a current note payable. Long-term debt is covered in depth in Long-Term Liabilities. For now, know that for some debt, including short-term or electric current, a formal contract might exist created. This contract provides additional legal protection for the lender in the issue of failure by the borrower to make timely payments. Also, the contract often provides an opportunity for the lender to actually sell the rights in the contract to another party.
An invoice from the supplier (such as the one shown in (Effigy)) detailing the purchase, credit terms, invoice appointment, and aircraft arrangements volition suffice for this contractual relationship. In many cases, accounts payable agreements do not include interest payments, unlike notes payable.
Accounts Payable. Contract terms for accounts payable transactions are usually listed on an invoice. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC By-NC-SA four.0 license)

For example, assume the possessor of a article of clothing boutique purchases hangers from a manufacturer on credit. The organizations may institute an ongoing purchase agreement, which includes purchase details (such every bit hanger prices and quantities), credit terms (two/10, n/60), an invoice appointment, and shipping charges (complimentary on lath [FOB] shipping) for each guild. The basics of shipping charges and credit terms were addressed in Merchandising Transactions if y'all would similar to refresh yourself on the mechanics. As well, to review accounts payable, you tin can also return to Merchandising Transactions for detailed explanations.
Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue, also known as deferred acquirement, is a client's accelerate payment for a product or service that has all the same to be provided by the company. Some common unearned revenue situations include subscription services, gift cards, accelerate ticket sales, lawyer retainer fees, and deposits for services. Every bit y'all learned when studying the accounting cycle (Analyzing and Recording Transactions, The Adjustment Procedure, and Completing the Accounting Bicycle), we are applying the principles of accrual accounting when revenues and expenses are recognized in different months or years. Under accrual accounting, a company does not record revenue equally earned until it has provided a production or service, thus adhering to the revenue recognition principle. Until the customer is provided an obligated product or service, a liability exists, and the amount paid in accelerate is recognized in the Unearned Acquirement account. Every bit soon as the company provides all, or a portion, of the production or service, the value is then recognized equally earned acquirement.
For case, presume that a landscaping company provides services to clients. The company requires advance payment before rendering service. The client's advance payment for landscaping is recognized in the Unearned Service Acquirement account, which is a liability. Once the visitor has finished the customer's landscaping, information technology may recognize all of the accelerate payment as earned revenue in the Service Revenue account. If the landscaping company provides part of the landscaping services within the operating period, it may recognize the value of the work completed at that time.
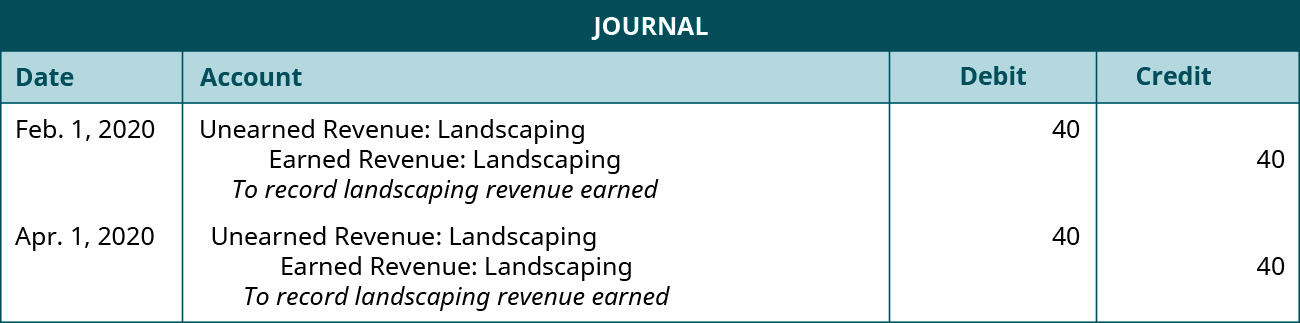
Perhaps at this point a simple example might help clarify the treatment of unearned acquirement. Assume that the previous landscaping visitor has a three-part plan to prepare lawns of new clients for next yr. The program includes a treatment in November 2019, Feb 2020, and Apr 2020. The visitor has a special rate of ?120 if the client prepays the entire ?120 earlier the November handling. In real life, the visitor would hope to have dozens or more customers. However, to simplify this example, we analyze the periodical entries from one client. Assume that the client prepaid the service on Oct fifteen, 2019, and all three treatments occur on the first day of the month of service. We also presume that ?40 in revenue is allocated to each of the 3 treatments.
Before examining the journal entries, we need some key information. Because office of the service will be provided in 2019 and the rest in 2020, we need to exist careful to keep the recognition of acquirement in its proper period. If all of the treatments occur, ?40 in revenue volition be recognized in 2019, with the remaining ?80 recognized in 2020. As well, since the customer could asking a refund before whatever of the services take been provided, we demand to ensure that nosotros do non recognize revenue until it has been earned. While it is nice to receive funding earlier y'all take performed the services, in essence, all yous have received when you get the coin is a liability (unearned service revenue), with the hope of it eventually becoming revenue. The following journal entries are built upon the customer receiving all three treatments. First, for the prepayment of future services and for the revenue earned in 2019, the journal entries are shown.

For the revenue earned in 2020, the journal entries would exist.
Advance Ticket Sales. Season ticket sales are considered unearned acquirement considering customers pay for them in advance of any games played. (credit: "Fans in Razorback Stadium (Fayetteville, AR)" by Rmcclen/Wikimedia Eatables, Public Domain)

Thinking almost Unearned Acquirement
When thinking nearly unearned revenue, consider the example of Amazon.com, Inc. Amazon has a large business portfolio that includes a widening presence in the online product and service space. Amazon has two services in particular that contribute to their unearned revenue account: Amazon Web Services and Prime membership.
Co-ordinate to Business concern Insider, Amazon had ?4.8 billion in unearned revenue recognized in their quaternary quarter report (December 2016), with almost of that contribution coming from Amazon Web Services.1 This is an increase from prior quarters. The growth is due to larger and longer contracts for web services. The advance payment for web services is transferred to acquirement over the term of the contract. The same is true for Prime membership. Amazon receives ?99 in advance pay from customers, which is amortized over the twelve-month period of the service agreement. This means that each month, Amazon only recognizes ?eight.25 per Prime membership payment as earned revenue.
Current Portion of a Notation Payable
A annotation payable is a debt to a lender with specific repayment terms, which can include principal and involvement. A annotation payable has written contractual terms that make it available to sell to another political party. The principal on a annotation refers to the initial borrowed amount, not including interest. In addition to repayment of principal, interest may accumulate. Interest is a monetary incentive to the lender, which justifies loan risk.
Let'south review the concept of interest. Interest is an expense that yous might pay for the use of someone else's money. For example, if y'all have a credit card and you owe a residue at the end of the calendar month it will typically accuse y'all a pct, such equally 1.five% a month (which is the same as xviii% annually) on the balance that you owe. Assuming that y'all owe ?400, your interest charge for the calendar month would be ?400 × i.5%, or ?6.00. To pay your residuum due on your monthly statement would require ?406 (the ?400 balance due plus the ?6 interest expense).
We make ane more observation about interest: interest rates are typically quoted in annual terms. For example, if you borrowed coin to buy a car, your interest expense might be quoted as 9%. Notation that this is an annual rate. If you are making monthly payments, the monthly charge for interest would be 9% divided by twelve, or 0.75% a calendar month. For example, if you borrowed ?20,000, and made sixty equal monthly payments, your monthly payment would be ?415.17, and your interest expense component of the ?415.17 payment would exist ?150.00. The formula to calculate interest on either an annual or partial-year basis is:

In our example this would be
\(?20,000\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}9%\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{12}=?150\)
The good news is that for a loan such every bit our car loan or even a home loan, the loan is typically what is chosen fully amortizing. At this point, you just need to know that in our case the amount that you owe would go from a residue due of ?20,000 down to ?0 after the twentieth payment and the function of your ?415.17 monthly payment allocated to interest would be less each month. For example, your final (sixtieth) payment would simply incur ?three.09 in interest, with the remaining payment covering the concluding of the principle owed. See (Figure) for an exhibit that demonstrates this concept.
Applying Amortization
Car loans, mortgages, and education loans have an amortization process to pay down debt. Amortization of a loan requires periodic scheduled payments of main and interest until the loan is paid in total. Every menses, the same payment amount is due, but involvement expense is paid offset, with the remainder of the payment going toward the master balance. When a customer start takes out the loan, nearly of the scheduled payment is made upwards of interest, and a very minor amount goes to reducing the master balance. Over time, more of the payment goes toward reducing the main rest rather than interest.
For example, let's say you have out a car loan in the amount of ?10,000. The annual interest rate is 3%, and you are required to make scheduled payments each calendar month in the amount of ?400. You first need to determine the monthly interest rate by dividing iii% by twelve months (three%/12), which is 0.25%. The monthly interest rate of 0.25% is multiplied past the outstanding principal residual of ?10,000 to go an interest expense of ?25. The scheduled payment is ?400; therefore, ?25 is applied to interest, and the remaining ?375 (?400 – ?25) is applied to the outstanding master balance. This leaves an outstanding principal balance of ?ix,625. Next calendar month, interest expense is computed using the new main balance outstanding of ?9,625. The new interest expense is ?24.06 (?9,625 × 0.25%). This means ?24.06 of the ?400 payment applies to involvement, and the remaining ?375.94 (?400 – ?24.06) is practical to the outstanding principal balance to get a new balance of ?9,249.06 (?9,625 – ?375.94). These computations occur until the unabridged main balance is paid in full.
A note payable is commonly classified as a long-term (noncurrent) liability if the note menstruation is longer than one year or the standard operating period of the visitor. However, during the company'south current operating menstruum, any portion of the long-term note due that will be paid in the current period is considered a current portion of a note payable. The outstanding rest annotation payable during the current period remains a noncurrent notation payable. Notation that this does non include the interest portion of the payments. On the balance sheet, the electric current portion of the noncurrent liability is separated from the remaining noncurrent liability. No periodical entry is required for this distinction, just some companies cull to bear witness the transfer from a noncurrent liability to a current liability.
For example, a bakery visitor may demand to take out a ?100,000 loan to keep business operations. The bakery's outstanding note chief is ?100,000. Terms of the loan crave equal annual primary repayments of ?10,000 for the next ten years. Payments volition exist made on July 1 of each of the ten years. Fifty-fifty though the overall ?100,000 notation payable is considered long term, the ?10,000 required repayment during the visitor's operating cycle is considered current (brusk term). This means ?x,000 would be classified as the electric current portion of a noncurrent annotation payable, and the remaining ?90,000 would remain a noncurrent notation payable.
The portion of a notation payable due in the current period is recognized as current, while the remaining outstanding balance is a noncurrent note payable. For example, (Figure) shows that ?18,000 of a ?100,000 note payable is scheduled to be paid within the current period (typically within one year). The remaining ?82,000 is considered a long-term liability and will be paid over its remaining life.
Current Portion of a Noncurrent Notation Payable. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, nether CC BY-NC-SA four.0 license)
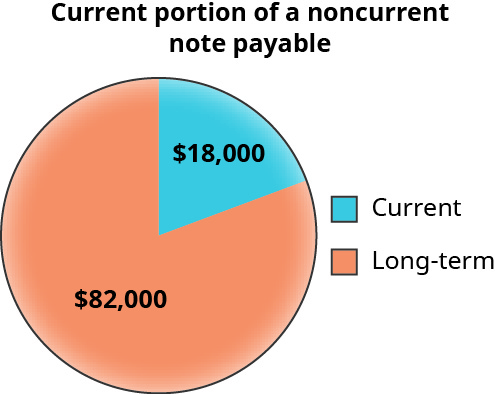
In addition to the ?eighteen,000 portion of the note payable that volition be paid in the electric current year, whatever accrued interest on both the current portion and the long-term portion of the notation payable that is due will also be paid. Assume, for example, that for the electric current twelvemonth ?7,000 of interest volition be accrued. In the current year the debtor volition pay a total of ?25,000—that is, ?7,000 in involvement and ?xviii,000 for the current portion of the note payable. A similar type of payment will be paid each year for as long as whatever of the note payable remains; still, the annual interest expense would exist reduced since the remaining note payable owed will exist reduced by the previous payments.
Involvement payable can also be a current liability if accrual of interest occurs during the operating period merely has nevertheless to be paid. An annual interest charge per unit is established every bit part of the loan terms. Interest accrued is recorded in Interest Payable (a credit) and Interest Expense (a debit). To summate interest, the company can use the following equations. This method assumes a twelve-month denominator in the adding, which means that we are using the calculation method based on a 360-day year. This method was more unremarkably used prior to the ability to practise the calculations using calculators or computers, because the calculation was easier to perform. However, with today'due south technology, information technology is more common to encounter the interest calculation performed using a 365-24-hour interval year. We will demonstrate both methods.

For example, we assume the baker has an annual involvement rate on its loan of 7%. The loan interest began accruing on July ane and it is now December 31. The bakery has accrued half dozen months of interest and would compute the interest liability every bit
\(?100,000\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}7%\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{6}{12}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}=?three,500\)
The ?iii,500 is recognized in Interest Payable (a credit) and Interest Expense (a debit).
Taxes Payable
Taxes payable refers to a liability created when a company collects taxes on behalf of employees and customers or for revenue enhancement obligations owed by the company, such equally sales taxes or income taxes. A future payment to a regime agency is required for the corporeality collected. Some examples of taxes payable include sales tax and income taxes.
Sales taxes result from sales of products or services to customers. A percentage of the sale is charged to the customer to cover the tax obligation (meet (Effigy)). The sales revenue enhancement rate varies by state and local municipalities but tin can range anywhere from 1.76% to well-nigh 10% of the gross sales price. Some states do not accept sales taxation because they desire to encourage consumer spending. Those businesses field of study to sales taxation hold the sales tax in the Sales Tax Payable account until payment is due to the governing body.
Sales Revenue enhancement. Many businesses are required to charge a sales tax on products or services sold. (credit: modification of "Sales Tax" by Kerry Ceszyk/Flickr, CC BY iv.0)
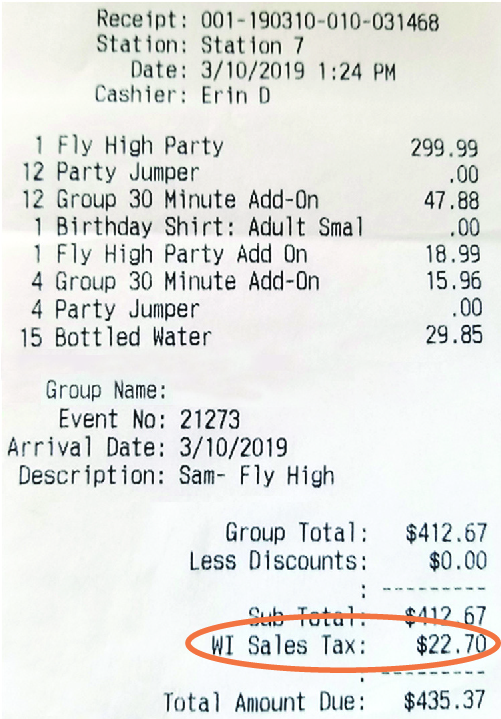
For example, assume that each time a shoe shop sells a ?l pair of shoes, information technology will accuse the customer a sales tax of 8% of the sales price. The shoe store collects a total of ?54 from the customer. The ?four sales tax is a current liability until distributed within the visitor's operating period to the government authority collecting sales revenue enhancement.
Income taxes are required to exist withheld from an employee'south salary for payment to a federal, state, or local dominance (hence they are known every bit withholding taxes). This withholding is a percent of the employee'due south gross pay. Income taxes are discussed in greater detail in Record Transactions Incurred in Preparing Payroll.
Primal Concepts and Summary
- Current liabilities are debts or obligations that ascend from past business activities and are due for payment within a company'south operating period (one year). Common examples of current liabilities include accounts payable, unearned revenue, the current portion of a noncurrent note payable, and taxes payable.
- Accounts payable is used to record purchases from suppliers on credit. Accounts payable typically does not include interest payments.
- Unearned revenue is recorded when customers pay in advance for products or services earlier receiving their benefits. The company maintains the liability until services or products are rendered.
- Notes payable is a debt to a lender with specific repayment terms, which can include principal and interest. Interest accrued can be computed with the annual interest rate, principal loan amount, and portion of the year accrued.
- Employers withhold taxes from employees and customers for payment to regime agencies at a afterward date, but within the concern operating flow. Common taxes are sales tax and federal, state, and local income taxes.
Multiple Selection
(Figure)Which of the post-obit is not considered a current liability?
- Accounts Payable
- Unearned Acquirement
- the component of a twenty-year note payable due in year 20
- current portion of a noncurrent annotation payable
C
(Figure)A company regularly purchases materials from a manufacturer on credit. Payments for these purchases occur inside the visitor's operating bike. They do not include interest and are established with an invoice outlining purchase details, credit terms, and shipping charges. Which current liability situation does this best describe?
- sales tax payable
- accounts payable
- unearned acquirement
- income taxes payable
(Figure)The following is selected fiscal data from Block Industries:
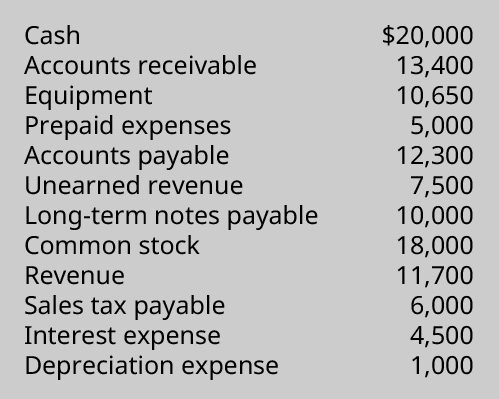
How much does Block Industries have in current liabilities?
- ?xix,800
- ?18,300
- ?12,300
- ?25,800
D
(Effigy)A ski visitor takes out a ?400,000 loan from a banking concern. The bank requires eight equal repayments of the loan main, paid annually. Assume no involvement is paid or accumulated on the loan until the last repayment. How much of the loan principal is considered a electric current portion of a noncurrent note payable in year three?
- ?l,000
- ?150,000
- ?100,000
- ?250,000
Questions
(Figure)Why is Accounts Payable classified as a current liability?
Accounts Payable can be fix every bit a line of credit between a purchaser and a supplier. The terms of the invoice usually land that payment is due inside a year, or a shorter fourth dimension frame. Since accounts payable amounts are due within a company'due south operating cycle, this account blazon would be considered a current liability.
(Figure)On which financial statement are current liabilities reported?
(Figure)What is the deviation between a noncurrent liability and a electric current liability?
A noncurrent liability is due in more than ane year or exterior a standard company operating flow. A electric current liability is payable within a company's operating flow, or less than a year.
(Effigy)How is the sales revenue enhancement rate usually determined? Does the company get to continue the sales tax equally earned revenue?
Practise Gear up A
(Effigy)Campus Flights takes out a bank loan in the amount of ?200,500 on March 1. The terms of the loan include a repayment of primary in ten equal installments, paid annually from March 1. The annual interest rate on the loan is 8%, recognized on December 31. (Round answers to the nearest whole dollar if needed.)
- Compute the involvement recognized as of December 31 in year 1 rounded to the whole dollar.
- Compute the principal due in year 1.
(Effigy)Consider the following accounts and determine if the account is a current liability, a noncurrent liability, or neither.
- greenbacks
- federal income taxation payable this year
- long-term note payable
- current portion of a long-term note payable
- note payable due in four years
- interest expense
- land income revenue enhancement
(Figure)Lamplight Plus sells lamps to consumers. The visitor contracts with a supplier who provides them with lamp fixtures. In that location is an agreement that Lamplight Plus is non required to provide cash payment immediately and instead will provide payment within xxx days of the invoice date.
Additional data:
- Lamplight purchases xxx light fixtures for ?20 each on Baronial ane, invoice date Baronial i, with no discount terms
- Lamplight returns ten light fixtures (receiving a credit corporeality for the total buy cost per fixture of ?twenty each) on August three.
- Lamplight purchases an additional fifteen low-cal fixtures for ?15 each on August 19, invoice appointment August 19, with no disbelieve terms.
- Lamplight pays ?100 toward its account on August 22.
What amount does Lamplight Plus still owe to the supplier on August 30? What account is used to recognize this outstanding amount?
Practise Ready B
(Figure)Everglades Consultants takes out a loan in the amount of ?375,000 on April ane. The terms of the loan include a repayment of principal in viii, equal installments, paid annually from the April 1 date. The annual interest rate on the loan is 5%, recognized on December 31. (Round answers to the nearest cent, if needed.)
- Compute the interest recognized as of Dec 31 in year ane.
- Compute the primary due in year 1.
(Figure)Match each of the following accounts with the appropriate transaction or description.
| A. Sales Tax Payable | i. A client pays in advance for services |
| B. Income Taxes Payable | 2. A run a risk incentive rate for a loan |
| C. Electric current portion of a long-term notation payable | iii. State withholding from an employee's paycheck |
| D. Interest Payable | iv. The portion of a notation due within the operating menstruation |
| E. Accounts Payable | v. A credit line between a purchaser and a supplier |
| F. Unearned Revenue | vi. Actress revenue enhancement collected on the sale of a product |
(Figure)Pianos Unlimited sells pianos to customers. The company contracts with a supplier who provides it with replacement pianoforte keys. There is an agreement that Pianos Unlimited is not required to provide cash payment immediately, and instead volition provide payment within thirty days of the invoice date.
Additional information:
- Pianos Unlimited purchases 400 piano keys for ?seven each on September 1, invoice appointment September i, with discount terms 2/10, north/30.
- Pianos Unlimited returns 150 piano keys (receiving a credit corporeality for the full purchase price per key of ?seven each) on September eight.
- The visitor purchases an boosted 230 keys for ?5 each on September xv, invoice engagement September 15, with no discount terms.
- The visitor pays 50% of the total amount due to the supplier on September 24.
What amount does Pianos Unlimited withal owe to the supplier on September 30? What account is used to recognize this outstanding corporeality?
Problem Set A
(Effigy)Consider the post-obit situations and determine (1) which type of liability should be recognized (specific account), and (2) how much should be recognized in the electric current period (twelvemonth).
- A business concern sets up a line of credit with a supplier. The company purchases ?10,000 worth of equipment on credit. Terms of purchase are five/10, n/30.
- A customer purchases a watering hose for ?25. The sales revenue enhancement charge per unit is 5%.
- Customers pay in advance for flavor tickets to a soccer game. There are xiv customers, each paying ?250 per flavor ticket. Each customer purchased two season tickets.
- A company issues 2,000 shares of its common stock with a cost per share of ?15.
(Figure)Stork Enterprises delivers care packages for special occasions. They charge ?45 for a small package, and ?80 for a large packet. The sales tax rate is half-dozen%. During the month of May, Stork delivers 38 modest packages and 22 large packages.
- What is the total revenue enhancement charged to the customer per small parcel? What is the overall charge per small packet?
- What is the full taxation charged to the customer per large package? What is the overall charge per large package?
- How much sales tax liability does Stork Enterprises take for the month of May?
- What account is used to recognize this tax situation for the month of May?
- When Stork remits payment to the sales tax governing torso, what happens to the sales tax liability?
Problem Prepare B
(Figure)Consider the following situations and determine (1) which type of liability should exist recognized (specific account), and (2) how much should exist recognized in the current period (year).
- A business concern depreciates a building with a book value of ?12,000, using straight-line depreciation, no save value, and a remaining useful life of 6 years.
- An arrangement has a line of credit with a supplier. The visitor purchases ?35,500 worth of inventory on credit. Terms of purchase are 3/20, n/60.
- An employee earns ?1,000 in pay and the employer withholds ?46 for federal income tax.
- A client pays ?4,000 in accelerate for legal services. The lawyer has previously recognized 30% of the services every bit revenue. The remainder is outstanding.
(Figure)Perfume Depot sells two unlike tiers of perfume products to customers. They charge ?thirty for tier 1 perfume and ?100 for tier 2 perfume. The sales tax rate is iv.5%. During the month of October, Perfume Depot sells 75 tier 1 perfumes, and sixty tier ii perfumes.
- What is the full taxation charged to the customer per tier 1 perfume? What is the overall charge per tier i category perfume?
- What is the total revenue enhancement charged to the customer per tier 2 perfume? What is the overall accuse per tier 2 category perfume?
- How much sales tax liability does Perfume Depot have for the calendar month of Oct?
- What business relationship is used to recognize this taxation situation for the month of October?
- When Perfume Depot remits payment to the sales tax governing torso, what happens to the sales tax liability?
Thought Provokers
(Figure)Research a Major League Baseball squad's season ticket prices. Pick 1 season ticket price level and answer the following questions:
- What team did you choose, and what are the ticket prices for a flavour?
- What is the sales tax rate for the buy of flavour tickets?
- How many games are included in the flavor package?
- What are the refund and exchange policies for purchases?
- What are some benefits to the team with customers paying in accelerate for season tickets?
- Explain in detail the unearned revenue liability created from season ticket sales.
- When does the team recognize this future revenue every bit earned?
- What effect does the refund or substitution policy have on the unearned acquirement account, and the power of the team to recognize revenue?
- If unearned revenue was split equally amongst all games (not including playoff games), how much would be recognized per game?
- Explain in detail the sales revenue enhancement liability created from season ticket sales.
- When does the team collect sales tax?
- What is the concluding purchase price of the season ticket with sales tax?
- Where does the squad recognize the sales tax liability (which statement and account[s])?
- To whom does the squad pay the sales taxation collected?
- When is sales tax payment required?
Footnotes
- oneEugene Kim. "An Disregarded Office of Amazon Will Be in the Spotlight When the Company Reports Earnings." Business Insider. April 28, 2016. https://world wide web.businessinsider.com/amazon-unearned-revenue-growth-shows-why-it-spent-more than-on-shipping-last-quarter-2016-4
Glossary
- account payable
- account for financial obligations to suppliers after purchasing products or services on credit
- current liability
- debt or obligation due inside one year or, in rare cases, a company'southward standard operating cycle, whichever is greater
- current portion of a note payable
- portion of a long-term note due during the company'southward electric current operating menstruum
- interest
- budgetary incentive to the lender, which justifies loan hazard; interest is paid to the lender past the borrower
- annotation payable
- legal document between a borrower and a lender specifying terms of a financial arrangement; in near situations, the debt is long-term
- principal
- initial borrowed amount of a loan, not including interest; as well, face up value or maturity value of a bond (the corporeality to exist paid at maturity)
- taxes payable
- liability created when a visitor collects taxes on behalf of employees and customers
- unearned acquirement
- advance payment for a product or service that has nonetheless to be provided past the company; the transaction is a liability until the product or service is provided
Which Of The Following Liabilities Is Created When A Company Receives Cash For Services,
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofaccountingv1openstax/chapter/identify-and-describe-current-liabilities/
Posted by: johnsensterst.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Liabilities Is Created When A Company Receives Cash For Services"
Post a Comment